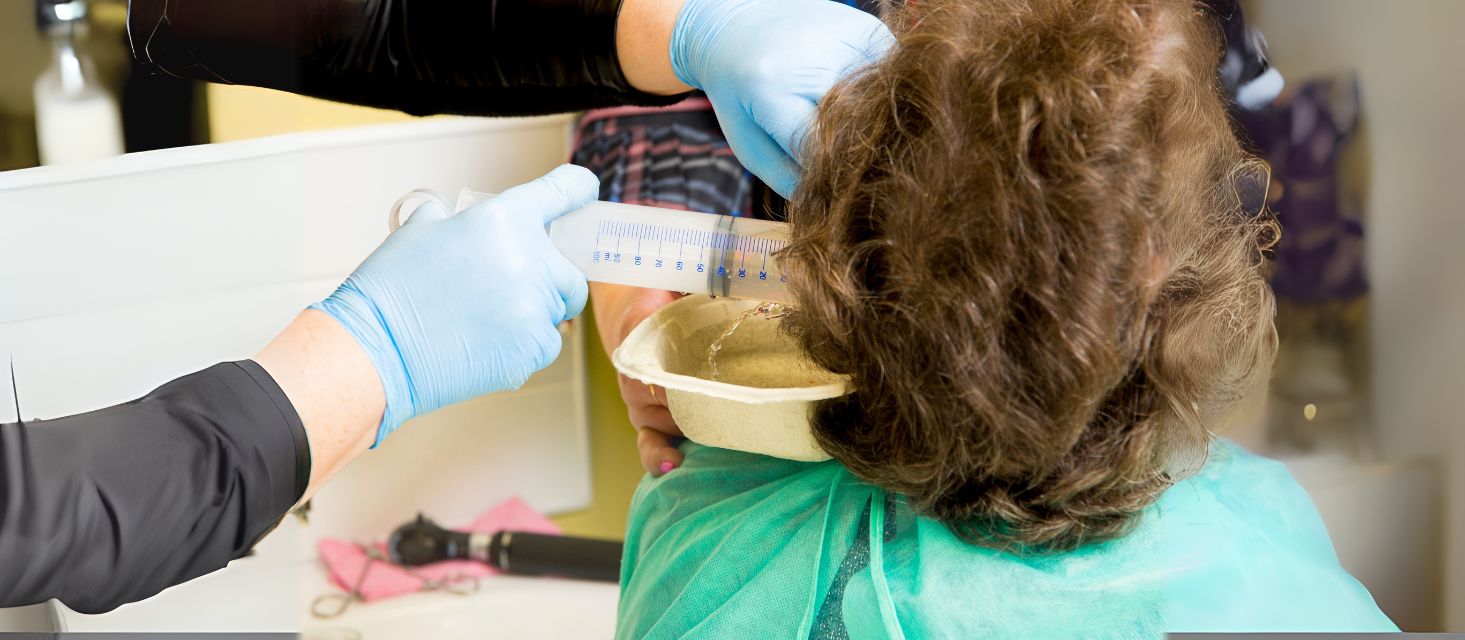
Ear syringing, also known as ear irrigation, is a common ear wax removal method used to clear blockages caused by excess ear wax in the ear canal. But who exactly performs this procedure? Typically, ear syringing can be carried out by various healthcare professionals, including general practitioners (GPs), ENT specialists, audiologists, and trained nurses. In some clinics, healthcare assistants trained in ear care may also perform the ear syringing procedure.
Moreover, with advancements in ear care technology, individuals can now perform ear syringing at home using specially designed tools. One such device is the Eddy ear irrigation tool developed by Auracle, which offers a safe and convenient way to manage earwax buildup under proper guidance. Learn more about ear cleaning techniques in this article.
What is Syringing Ear Wax?
Syringing earwax involves flushing the ear canal with a stream of water at body temperature to dislodge and remove hardened wax. Earwax, medically known as cerumen, serves as a protective barrier by trapping dust and preventing infections. However, when it accumulates excessively, it can cause several issues, including:
-
Blocked ears
-
Difficulty hearing
-
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
-
Earache or discomfort
-
Increased risk of infection
The ear syringing procedure typically includes the following steps:
-
Pre-treatment: Before syringing, ear drops such as olive oil or saline solution are used for a few days to soften the wax.
-
Irrigation: A specialised device sprays warm water into the affected ear, loosening and flushing out the wax.
-
Post-care: The healthcare professional examines the ear to ensure all wax is removed and provides aftercare advice to prevent future buildup.
When performed correctly, syringing is an effective treatment method for removing stubborn earwax and alleviating symptoms such as hearing loss and discomfort. For more detailed guidance, read our article on earwax blockage symptoms and treatment.
How to Soften Ear Wax Before Syringing
Softening earwax before syringing makes the procedure more effective and comfortable. Common methods for softening include:
-
Olive oil or mineral oil: Warm a few drops of oil and apply them twice a day for several days.
-
Hydrogen peroxide ear drops: These help break down hardened wax.
-
Saline solution: Products like Auracle’s saline sachets can be used to flush and soften wax before removal.
When applying drops, tilt your head so that the affected ear faces upward. Allow the solution to sit for a few minutes before draining. You can find suitable saline sachets for this purpose in Auracle’s product collection.
Benefits of Ear Syringing
There are several benefits to ear syringing, including:
-
Improved hearing: Removing excess wax can restore hearing clarity.
-
Reduced discomfort: Wax buildup can cause a feeling of fullness, itching, and even pain, which syringing can alleviate.
-
Lower risk of infection: By removing trapped debris and bacteria, syringing helps prevent infections like otitis externa.
-
Better balance: Excessive wax can affect balance, and removing it can help restore equilibrium.
For more on the benefits and risks, visit our ear irrigation guide.
Is Ear Syringing Safe?
Ear syringing is generally safe when performed by a professional or using a reliable at-home device. However, certain conditions may increase the risk of complications, such as:
-
Perforated eardrum
-
Recent ear surgery
-
History of recurrent ear infections
-
Presence of foreign objects in the ear
-
Mastoid cavity resulting from previous surgery
If you have any of these conditions, consult an ENT specialist before attempting ear syringing. Additionally, using appropriate tools like the Eddy ear irrigation tool, designed with safety features, ensures controlled water pressure and minimises risks. For more information, check out Auracle’s Eddy tool.
When Should You Consider Ear Syringing?
You should consider ear syringing if you experience any of the following symptoms:
-
Persistent build up of earwax despite using ear drops.
-
Blocked ears that interfere with your ability to hear.
-
Difficulty hearing or understanding conversations.
-
Tinnitus or ringing in the ears.
-
Pain, itching, or swelling in the ear.
If these symptoms occur, booking an appointment with a healthcare professional or trying an at-home solution like the Eddy may be beneficial. Learn when to clean your ears in this guide.
DIY Ear Syringing with Eddy
Auracle’s Eddy ear irrigation tool offers a professional-grade solution for at-home ear cleaning. Designed for safety and effectiveness, it includes features such as:
-
Adjustable water pressure for personalised comfort.
-
Customisable tips for different ear canal sizes.
-
A built-in temperature strip to ensure water is at body temperature.
-
A large water reservoir for continuous flushing.
The Eddy also comes with a 30-day money-back guarantee, free shipping, and a 2-year warranty, making it a reliable choice for those seeking to manage their ear health at home. Find out more about Auracle’s products.
Complications of Ear Syringing
While ear syringing is generally safe, complications can occasionally arise, including:
-
Infection: Improper technique or incomplete wax removal may lead to infection.
-
Swelling or irritation of the ear canal.
-
Perforated eardrum: Excessive pressure during irrigation can cause this serious complication.
-
Hearing loss: Rarely, incorrect procedures may result in temporary or permanent hearing loss.
To reduce the risk of complications, always follow proper guidelines and seek professional help if in doubt. For alternative methods, read about ear candling and its effectiveness.
Alternative Ear Wax Removal Methods
If syringing isn’t suitable, other ear wax removal methods include:
-
Microsuction: A gentle, precise method performed by ENT specialists using a small vacuum to remove wax.
-
Manual removal: Using specialised instruments, a healthcare provider manually extracts wax.
-
Ear drops: Over-the-counter ear drops can help dissolve and loosen wax over time.
For more on safe ear cleaning practices, visit this article.
Preventing Ear Wax Buildup
Preventive measures can help reduce the frequency of wax buildup:
-
Avoid using cotton buds, as they can push wax deeper into the ear canal.
-
Use ear drops regularly if you are prone to wax buildup.
-
Keep ears dry to prevent infections.
-
Seek professional cleaning periodically if you have recurrent wax issues or use hearing aids.
Loud and Clear: Final Thoughts
Ear syringing is a highly effective method for removing earwax and alleviating associated symptoms such as blocked ears, hearing loss, and discomfort. Whether performed by a healthcare professional or using advanced at-home devices like Auracle’s Eddy, ear syringing can significantly improve ear health. Always follow safety guidelines, and consult a professional if you have underlying ear conditions or concerns.
FAQs About Ear Syringing
1. What dissolves ear wax the fastest?
Hydrogen peroxide ear drops or specialised cerumenolytic agents are among the fastest ways to dissolve earwax. Olive oil is also effective when applied consistently over several days.
2. Can I syringe my ears if I have a perforated eardrum?
No, syringing is not recommended for individuals with a perforated eardrum as it can lead to serious complications. Consult an ENT specialist for alternative methods. Learn more about identifying ear infections in this guide.
3. Is ear syringing painful?
When done correctly, ear syringing is typically painless. You may feel a slight flushing sensation, but it should not cause pain. If you experience discomfort, stop the procedure and seek medical advice.
4. How often should I have my ears syringed?
The frequency depends on individual needs. Some patients may require it once or twice a year, while others may benefit from more regular cleaning if they have conditions like cleft palate or recurrent otitis externa.







Share:
Related Blogs
Hydrogen Peroxide in the Ear for Infection: What You Need to Know?
Crackling Noises in Ear: What You Need to Know